Free Energy By Radio Waves
Hi Guys welcome to my website this artical is about free energy.in this artical you can see all diagram about free energy generation regarding to like dish there are only three board are designed for generate free energy .

It aims to harvest energy from Radio Waves, mobile phone and broadcast signals to power the embedded sensors. ... The device, developed by Drayson Technologies, uses an antenna to gather radio wave energy from Radio Waves, mobile phone signals and broadcasts, and converts that into electricity.RF energy harvesting devices, such as Powercast’s Powerharvester® receivers, convert RF energy into DC power. These components are easily added to circuit board designs and work with standard or custom 50-ohm antennas. With current RF sensitivity of the P2110 Powerharvester receiver at -11dBm, powering devices or charging batteries at distances of 40-45 feet from a 3W transmitter is easily achieved and can be verified with Powercast’s development kits. Improving the RF sensitivity allows for RF-to-DC power conversion at greater distances from an RF energy source. However, as the range increases the available power and rate of charge decreases.
That is first circuit that will be setup in your home
Excess energy from transmitted communications signals can be captured and ... AM and FM radio waves to the many wireless devices that transmit signals around us, ... devices and possibly battery-free operation for some electronic devices. ... to some form of rectifying circuitry to convert the wireless energy to dc power.
Second circuit which is fitted into dish center
RF energy is currently broadcasted from billions of radio transmitters around the world, including mobile telephones, handheld radios, mobile base stations, and television/ radio broadcast stations. The ability to harvest RF energy, from ambient or dedicated sources, enables wireless charging of low-power devices and has resulting benefits to product design, usability, and reliability. Battery-based systems can be trickled charged to eliminate battery replacement or extend the operating life of systems using disposable batteries. Battery-free devices can be designed to operate upon demand or when sufficient charge is accumulated. In both cases, these devices can be free of connectors, cables, and battery access panels, and have freedom of placement and mobility during charging and usage.
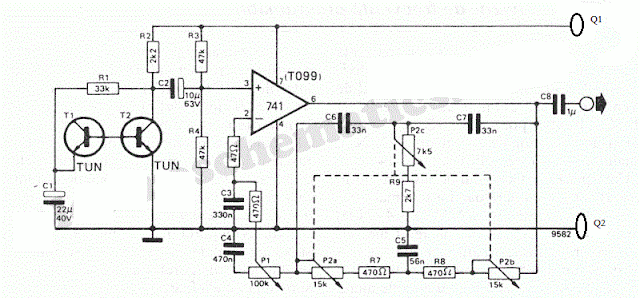
Third which is fitted into top of dish
he obvious appeal of harvesting ambient RF energy is that it is essentially “free” energy. The number of radio transmitters, especially for mobile base stations and handsets, continues to increase. ABI Research and iSupply estimate the number of mobile phone subscriptions has recently surpassed 5 billion, and the ITU estimates there are over 1 billion subscriptions for mobile broadband. Mobile phones represent a large source of transmitters from which to harvest RF energy, and will potentially enable users to provide power-on-demand for a variety of close range sensing applications. Also, consider the number of WiFi routers and wireless end devices such as laptops. In some urban environments, it is possible to literally detect hundreds of WiFi access points from a single location. At short range, such as within the same room, it is possible to harvest a tiny amount of energy from a typical WiFi router transmitting at a power level of 50 to 100 mW. For longer-range operation, larger antennas with higher gain are needed for practical harvesting of RF energy from mobile base stations and broadcast radio towers
RF energy can be broadcasted in unlicensed bands such as 868MHz, 915MHz, 2.4GHz, and 5.8GHz when more power or more predictable energy is needed than what is available from ambient sources. At 915MHz, government regulations limit the output power of radios using unlicensed frequency bands to 4W effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), as in the case of radio-frequency- identification (RFID) interrogators. As a comparison, earlier generations of mobile phones based on analog technology had maximum transmission power of 3.6W, and Powercast’s TX91501 transmitter that sends power and data is 3W
Hi Guys welcome to my website this artical is about free energy.in this artical you can see all diagram about free energy generation regarding to like dish there are only three board are designed for generate free energy .

It aims to harvest energy from Radio Waves, mobile phone and broadcast signals to power the embedded sensors. ... The device, developed by Drayson Technologies, uses an antenna to gather radio wave energy from Radio Waves, mobile phone signals and broadcasts, and converts that into electricity.RF energy harvesting devices, such as Powercast’s Powerharvester® receivers, convert RF energy into DC power. These components are easily added to circuit board designs and work with standard or custom 50-ohm antennas. With current RF sensitivity of the P2110 Powerharvester receiver at -11dBm, powering devices or charging batteries at distances of 40-45 feet from a 3W transmitter is easily achieved and can be verified with Powercast’s development kits. Improving the RF sensitivity allows for RF-to-DC power conversion at greater distances from an RF energy source. However, as the range increases the available power and rate of charge decreases.
That is first circuit that will be setup in your home
Excess energy from transmitted communications signals can be captured and ... AM and FM radio waves to the many wireless devices that transmit signals around us, ... devices and possibly battery-free operation for some electronic devices. ... to some form of rectifying circuitry to convert the wireless energy to dc power.
RF energy is currently broadcasted from billions of radio transmitters around the world, including mobile telephones, handheld radios, mobile base stations, and television/ radio broadcast stations. The ability to harvest RF energy, from ambient or dedicated sources, enables wireless charging of low-power devices and has resulting benefits to product design, usability, and reliability. Battery-based systems can be trickled charged to eliminate battery replacement or extend the operating life of systems using disposable batteries. Battery-free devices can be designed to operate upon demand or when sufficient charge is accumulated. In both cases, these devices can be free of connectors, cables, and battery access panels, and have freedom of placement and mobility during charging and usage.
Third which is fitted into top of dish
RF energy can be broadcasted in unlicensed bands such as 868MHz, 915MHz, 2.4GHz, and 5.8GHz when more power or more predictable energy is needed than what is available from ambient sources. At 915MHz, government regulations limit the output power of radios using unlicensed frequency bands to 4W effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), as in the case of radio-frequency- identification (RFID) interrogators. As a comparison, earlier generations of mobile phones based on analog technology had maximum transmission power of 3.6W, and Powercast’s TX91501 transmitter that sends power and data is 3W
How to program Attiny 85 with arduino uno









Comments
Post a Comment